
Absorption from the Digestive Tract (in vivo)
Normally, protein is absorbed as amino acids or short peptides after decomposition by various digestive enzymes in the stomach and the intestines, and mainly used as material for protein synthesis. When protein is absorbed in the form of peptides into the body, it is quicker than absorption of amino acids, and some of those peptides show bioactivity in the body.
Tripeptides in CTP-containing collagen are also expected to have rapid absorption and functionality. We studied the absorption of tripeptides in CTP from the digestive tract.
Test for absorption from the digestive tract
1) Methods
- <Test sample>
- Gly-Pro-Hyp; one of the major components of CTP-containing collagen, labeled with tritium(³H) was prepared as a test sample, and Proline; an amino acids, also labeled with tritium was prepared as a control.
- <Absorption from the digestive tract>
- Male rats at 5 weeks of age after fasting 16 hours were divided into 2 groups and administered 0.35 mmol/kg of the test samples orally. Blood samples were collected over time from those groups and monitored for radioactive concentration in the plasma, and examined for absorption of the test samples.
2) Results
Test result is shown in Figure 1. CTP was detected in the plasma 5 minutes after administration, and a concentration rise of CTP with time was observed. Furthermore, CTP was absorbed more quickly than proline as the control.
Figure 1: Absorption from the digestive tract (Variation of radioactive concentration in the plasma)
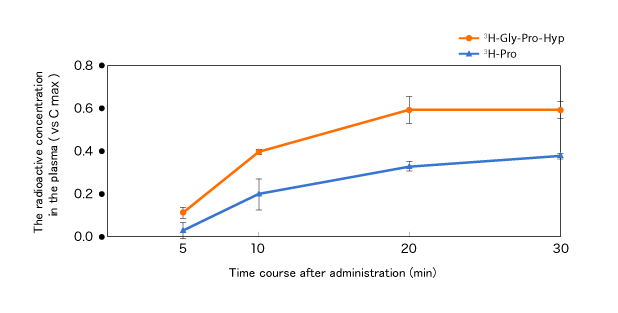
3) Discussion

CTP was absorbed into the blood vessel more quickly and effectively than amino acid molecules. Therefore, CTP is expected to promptly bring the benefits of collagen to the body.



