Kinetics in Blood (in vivo)
CTP was administered orally to one group of rats, and intraperitoneally to another. Then we analyzed tripeptides/dipeptides in those bloods and verified if there was any difference in absorption and metabolism whether the administration of CTP was passed through a digestive tract or not.
Test for kinetics in blood after oral administration of tripeptides (in rat)
1) Methods
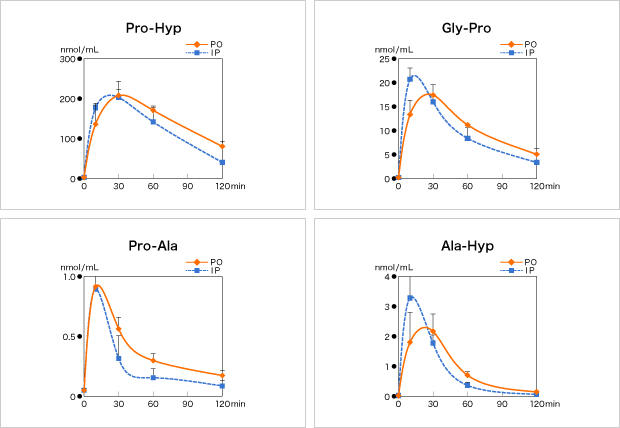
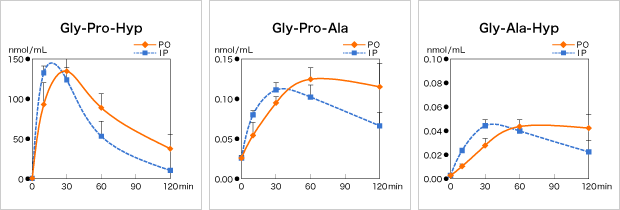
Wister rats at 9 weeks of age divided into 2 groups were administered CTP dissolved in normal saline orally (p.o.) and intraperitoneally (i.p.) at a dose of 125 mg/kg, respectively. Blood samples were collected with time from their caudal veins. Proteins were removed from the plasma by centrifugal separation of those samples, and were subjected to LC-MS/MS analysis. The following 7 components were measured: Gly-Pro-Hyp, Gly-Pro-Ala, and Gly-Ala-Hyp, which were main components of CTP-containing collagen, and Pro-Hyp, Pro-Ala, Gly-Pro, and Ala-Hyp, which were expected to occur as a result of metabolization of above tripeptides.
2) Results
The 3 main components of tripeptides (Gly-Pro-Hyp, Gly-Pro-Ala, and Gly-Ala-Hyp) moved to the plasma in both of p.o. and i.p. Those 3 tripeptides had similar patterns of increase and decrease in p.o. and i.p., and also showed similar results in Tmax, Cmax and AUC. Also 4 dipeptides (Pro-Hyp, Pro-Ala, Gly-Pro and Ala-Hyp) were detected which were expected to occur as metabolites in both of p.o. and i.p. As for Gly-Pro, only Tmax appeared earlier in i.p than in p.o., but there were no differences in Cmax and AUC between p.o. and i.p. The 3 other dipeptides showed close results of Tmax, Cmax and AUC in both of p.o. and i.p.
As described above, it was verified that tripeptides and dipeptides which were functional components of CTP-containing collagen were absorbed in blood in both oral and intraperitoneal administration.
3) Discussion
We confirmed that the oral administration of CTP could bring absorption of tripeptides and dipeptide at a high efficiency and speed equivalent to that achieved by the intraperitoneal administration.
* 3 components of tripeptides in blood (oral administration)
* 4 components of dipeptides of in blood (oral administration)