
Preventive /Improving effect on atherosclerosis (in vitro/in vivo)
Atherosclerosis arises from infiltration of macrophages associated with an inflammatory reaction of the arterial intima and the migration or proliferation of smooth muscle cells from media to intima in blood vessels. It is said that the lipid accumulation inside and outside of the cells of the arterial intima promote the lesion. We postulated that CTP-containing collagen might reduce serum cholesterol levels and inhibit proliferation of macrophage and smoothen muscle cells in order to inhibit the occurence and acceleration of atherosclerosis, and studied it in vitro and in vivo.
in vitro
1) Methods
To study the effect of CTP against migration and proliferation (a number of PCNA positive cell) of AoSMC, we prepared Transwell® with 8.0μm membrane filter and put human AoSMC of 1x106 cells/mL which was suspended in a basal medium to the upper chamber, and also put CTP or general CP of 3 to 300 μg/mL to the lower chamber, then incubated them at 37°C. The time course of migration and the number of PCNA positive cells of AoSMC was observed by the SDS-PAGE method and the immunoblot method.
2) Results
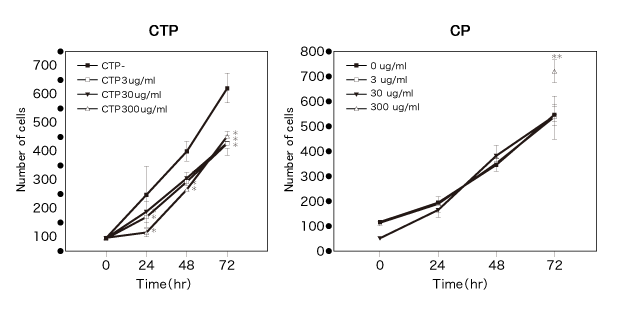
The CTP 3 to 300 μg/mL groups strongly inhibited migration of AoSMC after incubation for 48 hours, but the CP 3 to 300 μg/mL groups promoted it significantly in comparison with the control group (Figure 1). In addition, CTP apparently inhibited proliferation of AoSMC, but CP gave significant promotional effect on it after incubation for 72 hours only in 300 μg/mL addition (Figure 2).
Figure 1) Effect on migration of human AoSMC in vitro
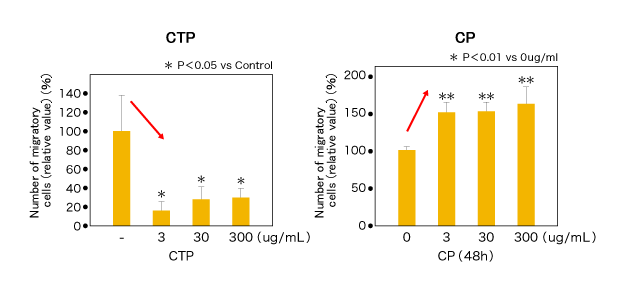
Figure 2) Effect on proliferation of human AoSMC in vitro
in vivo
1) Methods
A comparative examination was performed on total cholesterol level, the rate of incidence of atherosclerotic plaque, and histological findings between the CTP-containing collagen administered group and the control group of KHC rabbits at 3 months of age. KHC rabbits were prepared and divided into 2 groups : One was administered 200 mg/g of CTP-containing collagen orally for 3 months, and another was not administered any collagen to be a control, and then we observed total serum cholesterol (TCHO), atherosclerotic plaque and its fibrillation, and infiltration of macrophage (Mφ) and aortic smooth muscle cell (AoSMC) in both groups.
2) Results
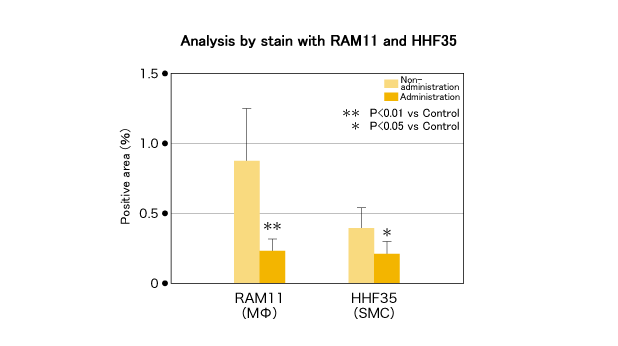
We found some atherosclerotic plaque in the control group, but found little of that in the CTP group (Figure 3). Regarding TCHO, there was little change in the control group, but it was deceased evidently in the CTP administered group (Figure 4). In addition, the CTP administered group showed significantly less filtration of Mφ and AoSMC in the plaque than that in the control group, and especially suggested inhibitory effect against filtration and outgrowth of Mφ (Figure 5).
Figure 3) Reduction effect of atherosclerotic plaque in the KHC rabbit
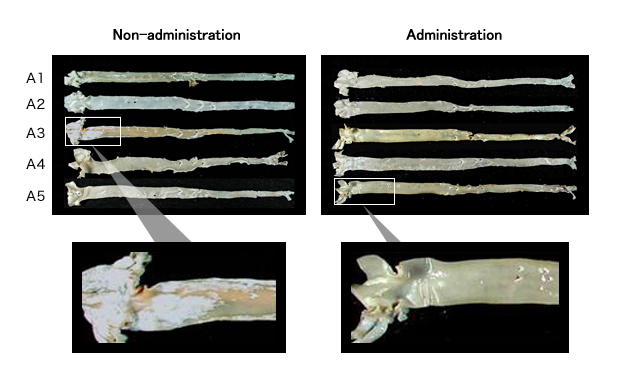
Figure 4) Effect on total serum cholesterol
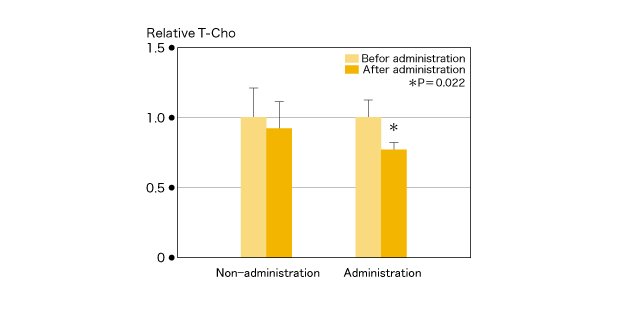
Figure 5) Effect on a number of macrophage (Mφ) and smooth muscle cell (SMC) in atherosclerotic plaque
3) Discussion

It is suggested strongly that ingestion of CTP could inhibit occurrence and advancement of atherosclerosis.



