
Promotion of hyaluronic acid production (in vitro)
Hyaluronic acid is a type of mucopolysaccharide, and is found largely in connective tissues in the body. It plays a key role along with collagen to maintain healthy skin. We studied how CTP affected hyaluronic acid production by using human normal skin-derived fibroblasts.
Test for promotion of hyaluronic acid production
1) Methods
- <Test sample>
- CTP was prepared as a test sample, purified water was used as a negative control, and N-acetylglucosamine (GlcNAc) was used as a positive control.
- <Measurement method>
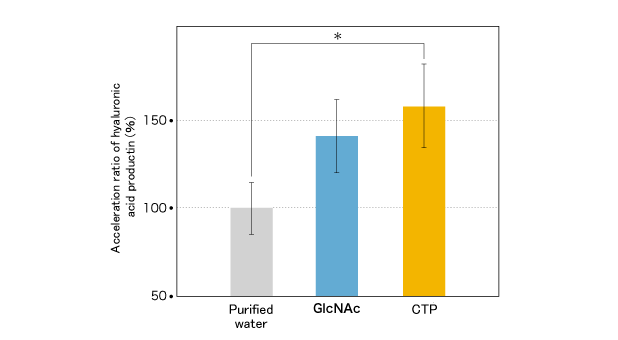
- Human normal skin-derived fibroblasts were sowed in each well of a 24-well plate at a concentration of 5x104 cells/mL, and cultivated for 3 days in 5% FCS-MEM under an environment of 5% CO2 at 37°C. After that, the medium was changed to 0.5% FCS-MEM. The test sample was added to the CTP groups at 0 or 10 μg/mL. Meanwhile, GlcNAc was added to the positive control group at 0.1 mM. 24 hours after addition, quantitative measurement of hyaluronic acid of each culture supernatant were performed by the sandwich method of binding protein using hyaluronan-binding protein (HABP) and biotin labeled HABP. The acceleration rate of hyaluronic acid production was indexed based on the quantity of hyaluronic acid in the negative control as 100%.
2) Results
The acceleration in rate of hyaluronic acid production is shown in the figure below. The quantity of hyaluronic acid was increased by about 1.5 times as a result of adding CTP, and that promotion effect was equal to or more than that of GlcNAc of the positive control.
The quantity of hyaluronic acid
3) Discussion

CTP increased the production amount of not only collagen but hyaluronic acid as well by activating human normal skin-derived fibroblasts. Therefore, we can expect that CTP-containing collagen will promote hyaluronic acid production in the skin and joints, and those effects will keep our skin healthy and make our joints move more smoothly.



