
Blood kinetics of collagen tripeptide containing collagen in human
Numerous reports exist on the absorbability of general collagen peptide (CP) after oral ingestion. Collagen tripeptide (CTP)-containing collagen is believed to be absorbed more efficiently because CTP is in tripeptide form and is absorbed directly through the small intestine.
In this page, we discuss the comparison of the plasma absorption of Gly-Pro-Hyp (GPHyp) and its metabolite Pro-Hyp (PHyp) after CP and CTP-containing collagen ingestion. GPHyp rarely appears after general CP ingestion but is a major component of CTP. PHyp is widely known as the main metabolite after CP ingestion.
Blood kinetics after the oral administration of CP or CTP-containing collagen in humans
1) Methods
We prepared porcine-derived CTP-containing collagen (Mw: 600 Da) and CP (Mw: 5,000) as test foods. Four healthy men participated in this ingestion test with at least a 2-week washout period between each administration. The subjects ingested 80 mg/kg body weight of a test food dissolved in water after a 16 h fasting period. Blood samples were withdrawn from the subjects’ forearms before and 5, 15, 30, 60, 120, and 240 min after ingestion. Then, the blood samples were centrifuged to obtain the plasma. GPHyp and PHyp in the plasma samples were subsequently analyzed via liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). The changes in the plasma levels and area under the curve (AUC) were calculated from the obtained data. An ingestion test with the tripeptide-rich fraction of the CTP-containing peptide was also performed.
2) Results
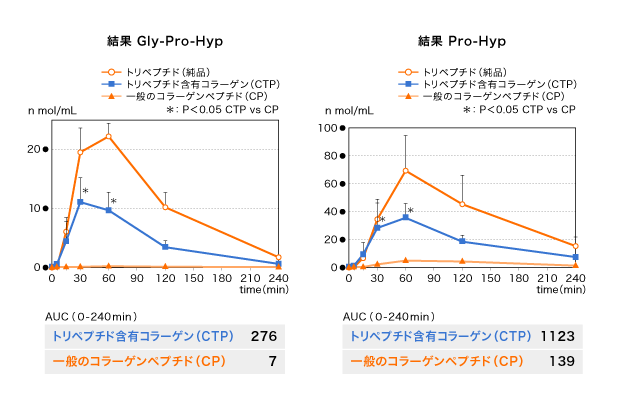
We report the results of the change in GPHyp plasma levels after the ingestion of the two test foods. GPHyp appeared in the blood 5 min after CTP-containing collagen ingestion. Subsequently, its plasma level rapidly increased and reached peak plasma concentration in 30–60 min. However, in CP ingestion, GPHyp plasma levels remained very low throughout the measurement period. AUC in CTP-containing collagen ingestion was approximately 39 times higher than that in CP ingestion.
Next, we discuss the change in PHyp plasma levels. PHyp appeared 5 min after CTP-containing collagen ingestion. Then, the plasma level rapidly increased and reached Tmax in 60 min. Consequently, PHyp gradually decreased but remained in the blood even at 240 min after CTP-containing collagen ingestion. AUC in CTP-containing collagen ingestion was approximately 8 times higher than that in CP ingestion.
Gly-Pro-Hyp、Pro-Hypの経時変化
3) Discussion
CTP-containing collagen was superior to general CP in terms of functional tripeptide/dipeptide absorbability and its high absorption provides reliable functionality.
4) Additional information
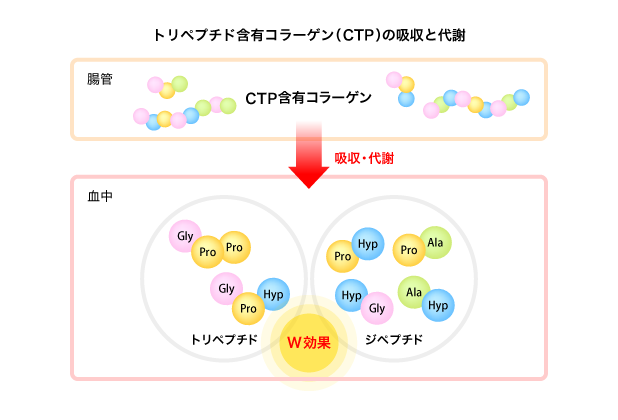
As shown in the Table below, various functional peptides appeared in the blood after the ingestion of CTP-containing collagen.
Table: Physiological activity of collagen-derived metabolite peptides.
| Peptides | Physiological activity |
|---|---|
| Gly-Pro-Hyp | Promotes collagen1-4) and hyaluronic acid production5), affects platelet aggregation6),and inhibits dipeptidylpeptidase-Ⅳ activity7) |
| Gly-Pro-Ala | Promotes nerve cell differentiation8) and alleviates intestinal damage9) |
| Gly-Pro | Hypotensive action10) |
| Pro-Hyp | Promotes proliferation of cultured fibroblasts11-12) and production of collagen13) and hyaluronic acid14) |
| Hyp-Gly | Suppresses osteoclast activation15) and promotes differentiation of osteoblasts16) and myoblasts17) |
| Leu-Hyp | Promotes collagen production18) |
| Ala-Hyp | Inhibits angiotensin-I-converting enzyme20-21), promotes collagen production 18) and cultured fibroblast proliferation11) |
| References: | |
| 1) | |
| 2) | |
| 3) | |
| 4) | |
| 5) | |
| 6) | Postlethwaite, A. E. "Snyderman. R. and Kang, AH." J. Exp. Med 144 (1976): 118. |
| 7) | |
| 8) | |
| 9) | |
| 10) | |
| 11) | |
| 12) | |
| 13) | |
| 14) | |
| 15) | Shigemura et al. Food Chemistry129(2011) |
| 16) | |
| 17) | |
| 18) | |
| 20) | |
| 21) | |



