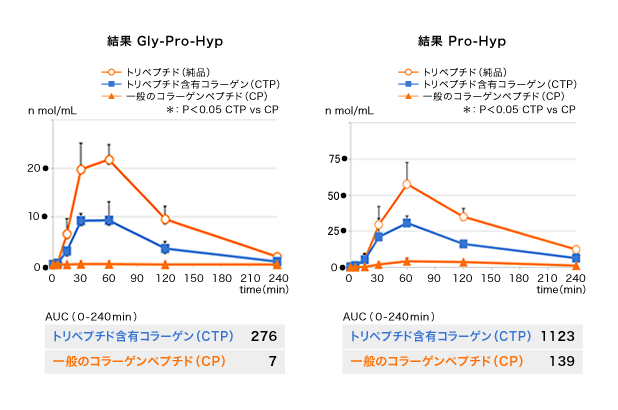
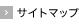GPHypはCTP含有コラーゲン摂取後5分で血中に出現しました。その後急激に上昇し、30-60分後に最大濃度に達しました。対してCP摂取では血中にごく微量が現れるのみであり、AUCはCTP含有コラーゲン摂取時の方がCP摂取時より数十倍高値でした。
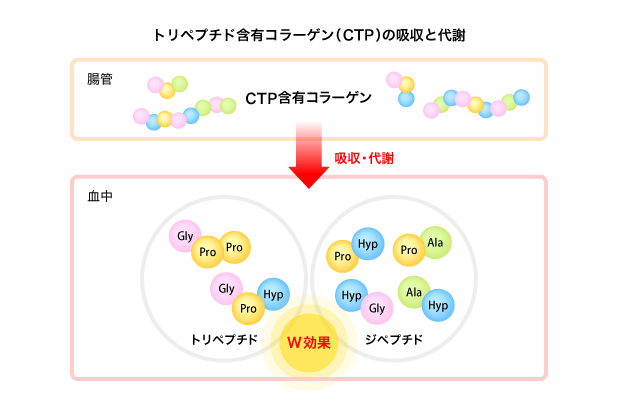
一方、PHypはCTP含有コラーゲン摂取後5分で血中に現れた後、急激に上昇して60分後に最大濃度に達し、その後緩やかに減衰して240分後も一部が血中に残留しました。PHypのAUCは、CTP含有コラーゲン摂取時の方がCP摂取時より数倍高値でした。
| 引用: |
| 1) |  Min, Geng. "Collagen hydrolysate Gly-Pro-Hyp on osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells." Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 1.3 (2017) Min, Geng. "Collagen hydrolysate Gly-Pro-Hyp on osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation of MC3T3-E1 cells." Journal of Clinical and Nursing Research 1.3 (2017) |
| 2) |  Lee, Hyun-Jun, et al. "Orally administered collagen peptide protects against UVB-induced skin aging through the absorption of dipeptide forms, Gly-Pro and Pro-Hyp." Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 83.6 (2019): 1146-1156. Lee, Hyun-Jun, et al. "Orally administered collagen peptide protects against UVB-induced skin aging through the absorption of dipeptide forms, Gly-Pro and Pro-Hyp." Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 83.6 (2019): 1146-1156. |
| 3) |  Tang, L., et al. "Effect of collagen tripeptide of Type I collagen on midration, proliferation and collagen synthesis of human aortic smooth muscle cells." J Kanazawa Med Univ 34 (2009): 93-100. Tang, L., et al. "Effect of collagen tripeptide of Type I collagen on midration, proliferation and collagen synthesis of human aortic smooth muscle cells." J Kanazawa Med Univ 34 (2009): 93-100. |
| 4) |  Tsuruoka, Naoki, et al. "Promotion by collagen tripeptide of type I collagen gene expression in human osteoblastic cells and fracture healing of rat femur." Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 71.11 (2007): 2680-2687. Tsuruoka, Naoki, et al. "Promotion by collagen tripeptide of type I collagen gene expression in human osteoblastic cells and fracture healing of rat femur." Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 71.11 (2007): 2680-2687. |
| 5) |  Okawa, Tomoko, et al. "Oral administration of collagen tripeptide improves dryness and pruritus in the acetone-induced dry skin model." Journal of Dermatological Science 66.2 (2012): 136-143. Okawa, Tomoko, et al. "Oral administration of collagen tripeptide improves dryness and pruritus in the acetone-induced dry skin model." Journal of Dermatological Science 66.2 (2012): 136-143. |
| 6) |  Postlethwaite, A. E., J. M. Seyer, and A. H. Kang. "Induction of fibroblast chemotaxis by type I, II and III collagens and collagen degradation peptides." Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75 (1978): 871. Postlethwaite, A. E., J. M. Seyer, and A. H. Kang. "Induction of fibroblast chemotaxis by type I, II and III collagens and collagen degradation peptides." Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 75 (1978): 871.
Postlethwaite, A. E. "Snyderman. R. and Kang, AH." J. Exp. Med 144 (1976): 118. |
| 7) |  Hatanaka, Tadashi, Kayoko Kawakami, and Misugi Uraji. "Inhibitory effect of collagen-derived tripeptides on dipeptidylpeptidase-Ⅳ activity." Journal of enzyme inhibition and medicinal chemistry 29.6 (2014): 823-828. Hatanaka, Tadashi, Kayoko Kawakami, and Misugi Uraji. "Inhibitory effect of collagen-derived tripeptides on dipeptidylpeptidase-Ⅳ activity." Journal of enzyme inhibition and medicinal chemistry 29.6 (2014): 823-828. |
| 8) |  特願2009-272229神経細胞分化促進剤 特願2009-272229神経細胞分化促進剤 |
| 9) |  Deng, Zhao, et al. "Gly-pro-ala peptide and FGSHF3 exert protective effects in DON-induced toxicity and intestinal damage via decreasing oxidative stress." Food Research International 139 (2021): 109840. Deng, Zhao, et al. "Gly-pro-ala peptide and FGSHF3 exert protective effects in DON-induced toxicity and intestinal damage via decreasing oxidative stress." Food Research International 139 (2021): 109840. |
| 10) |  Ichimura, Toshiaki, et al. "Antihypertensive effect of enzymatic hydrolysate of collagen and Gly-Pro in spontaneously hypertensive rats." Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 73.10 (2009): 2317-2319. Ichimura, Toshiaki, et al. "Antihypertensive effect of enzymatic hydrolysate of collagen and Gly-Pro in spontaneously hypertensive rats." Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 73.10 (2009): 2317-2319. |
| 11) |  Ohara, Hiroki, et al. "Collagen‐derived dipeptide, proline‐hydroxyproline, stimulates cell proliferation and hyaluronic acid synthesis in cultured human dermal fibroblasts." The Journal of dermatology 37.4 (2010): 330-338. Ohara, Hiroki, et al. "Collagen‐derived dipeptide, proline‐hydroxyproline, stimulates cell proliferation and hyaluronic acid synthesis in cultured human dermal fibroblasts." The Journal of dermatology 37.4 (2010): 330-338. |
| 12) |  Shigemura, Yasutaka, et al. "Effect of prolyl-hydroxyproline (Pro-Hyp), a food-derived collagen peptide in human blood, on growth of fibroblasts from mouse skin." Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 57.2 (2009): 444-449. Shigemura, Yasutaka, et al. "Effect of prolyl-hydroxyproline (Pro-Hyp), a food-derived collagen peptide in human blood, on growth of fibroblasts from mouse skin." Journal of agricultural and food chemistry 57.2 (2009): 444-449. |
| 13) |  Lee, Hyun-Jun, et al. "Orally administered collagen peptide protects against UVB-induced skin aging through the absorption of dipeptide forms, Gly-Pro and Pro-Hyp." Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 83.6 (2019): 1146-1156. Lee, Hyun-Jun, et al. "Orally administered collagen peptide protects against UVB-induced skin aging through the absorption of dipeptide forms, Gly-Pro and Pro-Hyp." Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 83.6 (2019): 1146-1156. |
| 14) |  Ohara, Hiroki, et al. "Collagen‐derived dipeptide, proline‐hydroxyproline, stimulates cell proliferation and hyaluronic acid synthesis in cultured human dermal fibroblasts." The Journal of dermatology 37.4 (2010): 330-338. Ohara, Hiroki, et al. "Collagen‐derived dipeptide, proline‐hydroxyproline, stimulates cell proliferation and hyaluronic acid synthesis in cultured human dermal fibroblasts." The Journal of dermatology 37.4 (2010): 330-338. |
| 15) |  Mano, H., Nakatani, S., Sekiguchi, Y., Shimizu, J., Sugihara, F.,Haketa, Y., and Wada, M., Abstr. 27th Annu. Meet. Jpn. Soc. Bone Miner. Res., p. 227, 2009 Mano, H., Nakatani, S., Sekiguchi, Y., Shimizu, J., Sugihara, F.,Haketa, Y., and Wada, M., Abstr. 27th Annu. Meet. Jpn. Soc. Bone Miner. Res., p. 227, 2009
Shigemura et al. Food Chemistry129(2011) |
| 16) |  Kimira, Yoshifumi, et al. "Collagen-derived dipeptide prolyl-hydroxyproline promotes differentiation of MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells." Biochemical and biophysical research communications 453.3 (2014): 498-501. Kimira, Yoshifumi, et al. "Collagen-derived dipeptide prolyl-hydroxyproline promotes differentiation of MC3T3-E1 osteoblastic cells." Biochemical and biophysical research communications 453.3 (2014): 498-501. |
| 17) |  Kitakaze, Tomoya, et al. "The collagen derived dipeptide hydroxyprolyl-glycine promotes C2C12 myoblast differentiation and myotube hypertrophy." Biochemical and biophysical research communications 478.3 (2016): 1292-1297. Kitakaze, Tomoya, et al. "The collagen derived dipeptide hydroxyprolyl-glycine promotes C2C12 myoblast differentiation and myotube hypertrophy." Biochemical and biophysical research communications 478.3 (2016): 1292-1297. |
| 18) |  特許第4995155号 生体コラーゲン合成促進剤並びに生体コラーゲン合成促進用飲食品、化粧品及び医薬部外品 特許第4995155号 生体コラーゲン合成促進剤並びに生体コラーゲン合成促進用飲食品、化粧品及び医薬部外品 |
| 20) |  岩井浩二, et al. "鶏コラーゲン加水分解物摂取後のヒト血中ペプチドの動態と ACE 阻害作用." 日本食品科学工学会誌 56.6 (2009): 326-330. 岩井浩二, et al. "鶏コラーゲン加水分解物摂取後のヒト血中ペプチドの動態と ACE 阻害作用." 日本食品科学工学会誌 56.6 (2009): 326-330. |
| 21) |  Oshima, Genichiro, Hirokazu Shimabukuro, and Kinzo Nagasawa. "Peptide inhibitors of angiotensin I-converting enzyme in digests of gelatin by bacterial collagenase." Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Enzymology 566.1 (1979): 128-137. Oshima, Genichiro, Hirokazu Shimabukuro, and Kinzo Nagasawa. "Peptide inhibitors of angiotensin I-converting enzyme in digests of gelatin by bacterial collagenase." Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Enzymology 566.1 (1979): 128-137. |